Lens into the Chinese Laser Industry
Since the invention of laser over 50 years ago, the technology has revolutionized to a broad range of applications and products across industries. The laser industry now has a complete and mature industry chain layout, including upstream laser materials and supporting components, the midstream laser beam sources and laser equipment and systems, as well as various downstream laser applications and consumption products across a broad range of industries.
This article will provide a synopsis on the laser industry in China through understanding:
- Development of Industrial Lasers,
- Our View of this Sector in China, and
- the ESG Benefits of Laser Technology.
Development of Industrial Laser Technology
Lasers provide flexible, non-contact, and high-speed ways to process and treat various materials, and are a key enabler of advanced manufacturing techniques, including automation and miniaturization. Therefore, industrial laser systems are continuously gaining share in the materials processing market within the automotive, aerospace, energy, electronics, consumer appliances, and heavy machinery sectors.
The integration of laser with other automation technologies, such as robotics and vision, enables new applications and enhances the utility of laser technology. Advances in laser and automation technologies reinforce each other. The speed and precision of laser processing are determined by not only the laser source, but also by the robot and machine tool it is integrated with. In high-power applications, thermal impact challenges motion control precision and stability and needs to be compensated for with advanced automation technologies. In other cases, sophisticated and novel motion control enhances laser material processing quality and expands its scope with the same laser source.
Our View
We believe that laser will consistently displace and outgrow conventional material processing technologies and become a crucial tool in factory automation. Fiber laser is the most important industrial laser type and should continue to take share from legacy types such as gas and solid-state lasers. By industry, the automotive industry is the largest customer, with the laser being used to make the car body and power train. Together with consumer electronics, these two sectors account for the bulk of demand, although other usages like welding, micromachining, and additive manufacturing are growing faster. In particular, the increasing complexity of the Apple iPhone in terms of functions and components involves more laser precision due to the form factor and a denser PCB (Printed Circuit Board). The miniaturization trend of the PCB drives adoption for more laser welding and drilling because of its higher precision in laser micromachining.
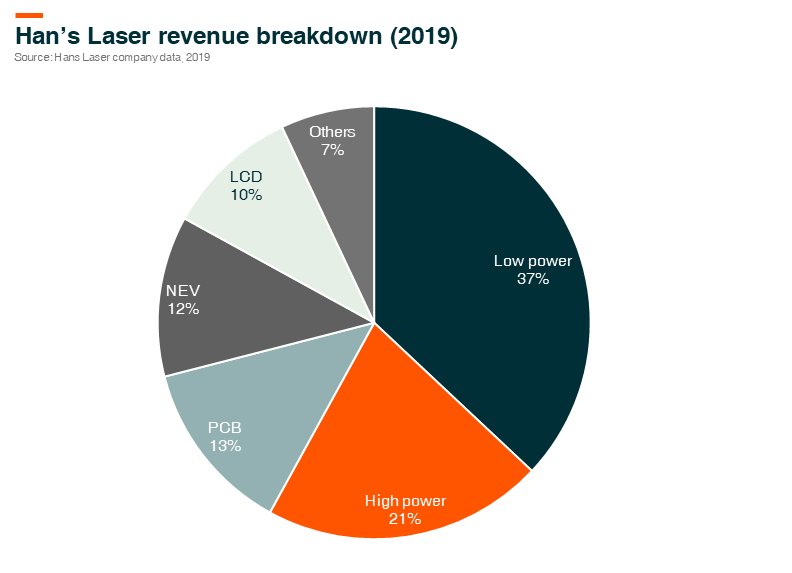
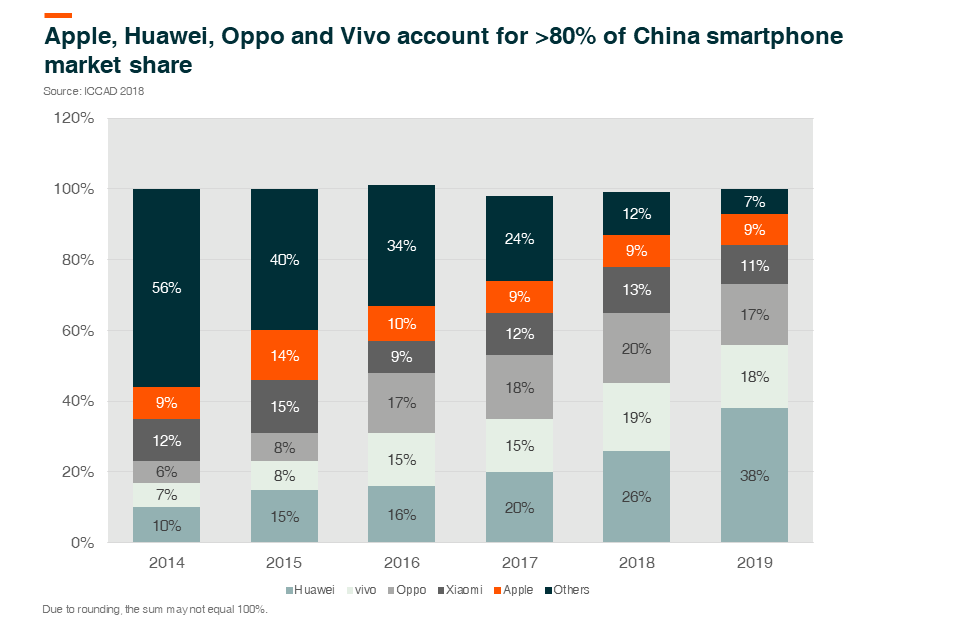
In particular, we believe that Hans Laser is a key beneficiary of iPhone model cycle changes. The company is the leading laser processing solution provider in China specializing in mobile devices such as smartphones, tablets and wearables. Key customers of Hans Laser for low-power laser (mostly smartphone related) include Apple, Huawei, Oppo and Vivo. The company also supplies to BOE Tech for LCD devices, Shengyi Tech and Kinwong Electronic in the PCB sector and CATL in the Electronic Vehicle (EV) space.
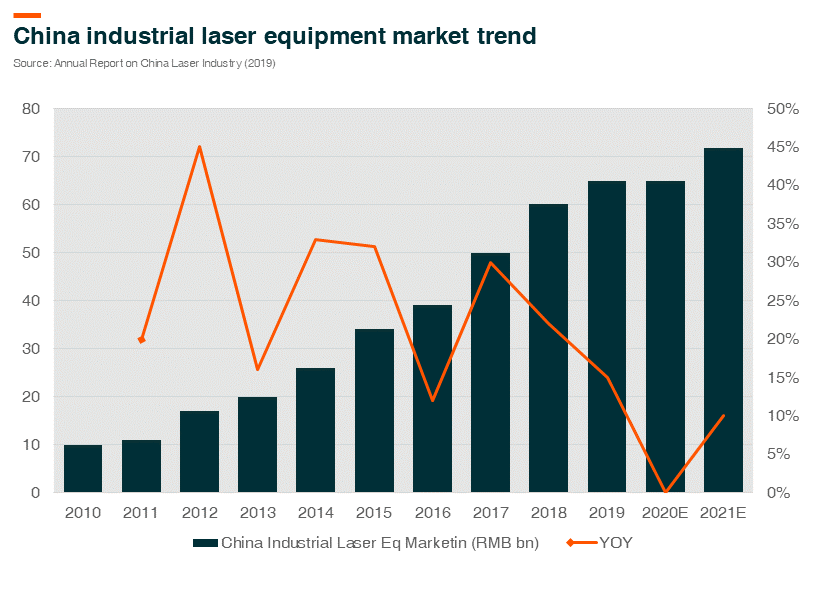
During the past few years, China has been the key driver of the global industrial laser equipment market with a remarkable Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR1) of 26.1% in 2011-17, far above the 11% CAGR of the global market. As of 2017, China accounted for approximately 43% of the global industrial laser equipment market, up from 18% as of 2010. In particular, China, as the major manufacturing base of the world, is considered to be the largest market for laser marking and metal cutting systems, while East Asia (Japan and South Korea) is the largest market for laser micro-processing and laser semiconductor processing equipment. The industrial laser market in China is expected to be impacted this year by the pandemic, though we should see a resumption of growth in 2021.
The outperformance of the China industrial laser market is also evidenced by the growing contribution of the market in the revenue mix of IPG Photonics Co. (“IPG”2), the global leader in high-power fiber lasers, the most popular laser solutions in general manufacturing industrials. IPG registered a CAGR of 24.8% in total revenue in 2011-17, within which, China delivered a CAGR of 40.4%, with revenue contribution rising to 44% as of 2017, up from 19% as of 2010. However, the trade war has had a widespread impact on investment decisions of general manufacturers in China since 2H18, in addition to the down-cycle of consumer electronics. These are two major downstream demand sources for China’s industrial laser equipment.
As at November 2019, fiber lasers have now become the main laser source for material processing in China, accounting for more than 60%3 of the laser processing market. The positive effect of the laser price reduction is the rapid spread of applications where prices are sensitive to end users, especially in metal cutting, marking, and cleaning. In 2018, 30,000 units of mid-power and 6000 units of high-power laser cutting systems, as well as 130,000 units of laser markers, were sold in China.
According to the Annual Report on the China Laser Industry, as of 2017, China’s low-power fiber laser source (<100W) localization rate reached approximately 93%, rapidly rising from 63% as of 2014. Meanwhile, the localization rates of mid/high-power fiber laser source (100W-1.5KW) and high-power fiber laser source (>1.5KW) rose to 63% and 10% as of 2017, from 17% and 1% as of 2013 respectively. Along this trajectory, we think there is significant room for domestic fiber lasers to further substitute the imported mid to high power fiber lasers going forward.
In our view, the key competitive advantages of Chinese fiber laser source makers include:
- Favorable Market Access – Chinese makers have favorable market access since China is a major manufacturing base in the world, as well as the largest market for laser marking and metal cutting systems with faster growing demand on laser applications
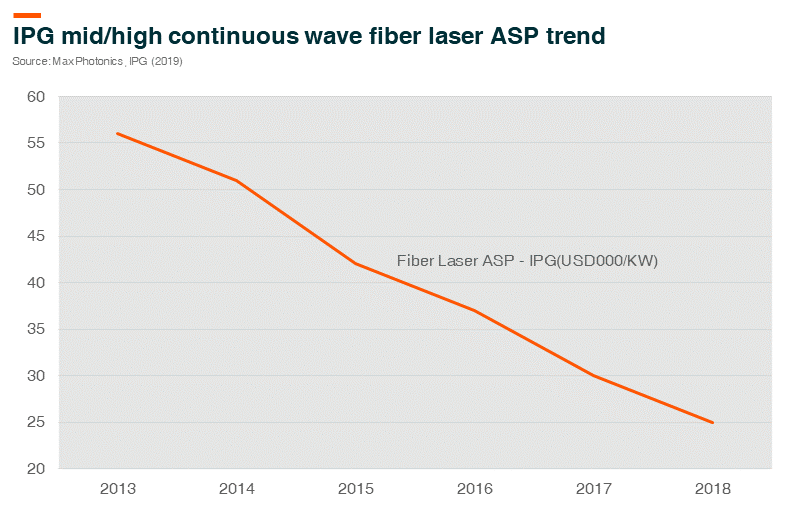
- Attractive Average Selling Price (ASP) – Chinese players have achieved an attractive ASP discount to foreign leading players such as IPG. IPG indicated a 17% CAGR of continuous wave (“CW”) fiber laser, ASP declined in 2015-18; while some Chinese fiber laser makers saw CAGR declined of approximately 25%. That said, the ASP gap of fiber lasers between Chinese players and IPG has been widening, thanks to both raw material unit cost savings and RMB/USD FX rate depreciation.
However, we believe in the next five to ten years IPG should be able to maintain its market position in the high-end fiber laser market. There is still a significant technology gap between IPG and Raycus, a leading Chinese fiber laser source maker. IPG has completed the R&D (Research & Development) for up to 120KW CW ytterbium fiber lasers and up to 20KW single-mode and low-mode output ytterbium fiber lasers. It has achieved the commercial production for 15-20KW CW fiber lasers, while seeing drastic sales expansion for 6KW and above CW fiber lasers in the cutting applications. That said, we believe Chinese fiber laser source makers, spearheaded by Raycus, have managed to narrow the gap with IPG and should continue to outperform in shipment volume in the near future by offering higher quality/price fiber lasers with elevating power levels.
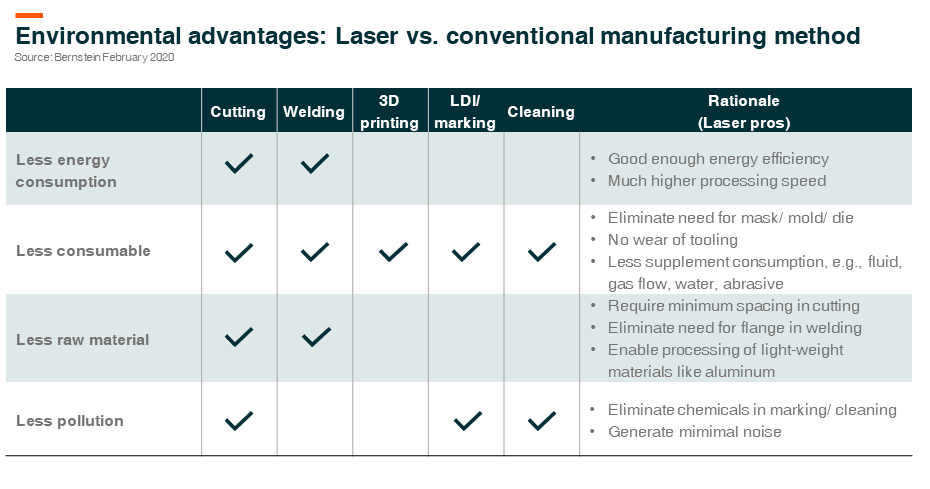
ESG Benefits of Industrial Lasers
From an ESG perspective, there are significant positives using laser as compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Firstly, due to more concentrated energy delivery and much faster processing speed in cutting and welding, fiber laser saves 70-90% of total energy consumption compared to conventional methods, such as punch press and arc welding. Secondly, laser reduces the use of costly and hard-to-make physical templates, tooling, and supplements, therefore reducing the environmental footprint. Thirdly, thanks to its flexibility and precision, laser material processing is key in its technology in reducing waste and scrap, hence saving raw materials. Furthermore, laser also enables the use of innovative materials (e.g. aluminum, plastic, and composite) that are lighter and stronger, but difficult to process with legacy cutting and welding methods. Finally, laser replaces chemicals in marking and metal surface cleaning. It also saves hundreds of millions in tons of water used to treat these chemicals every year.
In conclusion, we believe there is still headroom for growth in the industrial laser industry in China. Although market share is still dominated by foreign players like IPG, many Chinese local players are catching up in their respective target markets and are expected to benefit from this growing sector.
Global X China Robotics and AI Brand ETF (2807 HKD / 9807 USD), seeks to deliver the performance of the FactSet China Robotics and artificial Intelligence Index, enabling investors to access to high growth potential through companies critical to the development of robotics and artificial intelligence in China.
Other Key Features of Global X China Robotics and AI ETF:
- Unconstrained Approach: The fund’s composition transcends classic sector and industry classifications by tracking an emerging theme.
- ETF Efficiency: In a single trade, the fund delivers access to dozens of companies with high exposure to the robotics and artificial intelligence theme in China.
Please click here for more information on the Global X China Robotics and AI ETF.